You hear about lithium batteries everywhere, but also see alarming headlines. This confusion makes you hesitant, potentially causing you to miss out on huge gains in performance and savings.
Lithium batteries are a superior power technology offering more energy in a lighter package for a much longer lifespan. Their main historical issue, safety, has been overcome with safer chemistries and smart electronics, making them the reliable choice for critical applications.

Transition Paragraph:
In my ten years as a UPS manufacturer at Daopulse, I've seen the industry transform. We used to only talk about lead-acid. Now, clients like Mr. Li, who procures systems for hospitals, come to us with questions about lithium. They want to know the real story behind the headlines. They need to be sure they're making a safe, reliable investment for their critical infrastructure. Let's break down the most common questions I hear.
What Is the Biggest Problem with Lithium Batteries?
You’ve seen news reports of lithium batteries catching fire. This makes you nervous about using them in a data center or medical facility where failure is not an option.
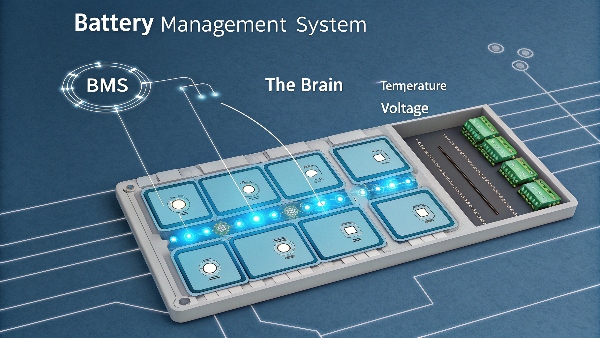
The biggest historical problem is "thermal runaway," a chain reaction causing extreme overheating. This is now solved in high-quality batteries by using safer chemistries like LiFePO4 and a smart Battery Management System (BMS) that actively prevents hazardous conditions.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
Thermal runaway is the issue that created all the negative headlines. It happens when a cell inside a battery pack gets damaged or overcharged, causing it to heat up rapidly. This heat can spread to neighboring cells, creating a dangerous, self-sustaining fire. However, it's crucial to understand that this is not a problem with all lithium batteries. The issue was most common in older, high-energy-density chemistries used in consumer gadgets.
For industrial applications like the UPS systems we design, we use a much safer chemistry called Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). It is chemically far more stable and resistant to overheating. More importantly, every battery pack we build includes a Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS is the battery’s brain. It constantly monitors the temperature, voltage, and current of every single cell. If it detects any unsafe condition, like a potential overcharge, it will instantly cut the power to protect the system. This combination of a stable chemistry and an intelligent BMS makes thermal runaway exceptionally rare in a modern, well-engineered UPS. My key insight is this: The application range of lithium batteries is constantly expanding, and their safety performance is becoming more and more reliable.
What Is a Disadvantage of Lithium Batteries?
You see the higher price tag on a lithium-ion UPS. This initial cost makes you pause and question if it's the right choice for your project's budget.
The main disadvantage of lithium-ion batteries is their higher upfront purchase cost compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. However, this is not their true long-term cost, which is actually much lower due to their vastly superior lifespan and zero maintenance.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
I always have a direct conversation with procurement managers about the price. Yes, a lithium-ion UPS costs more on day one. But a smart manager looks at the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the project's lifetime. A lead-acid battery needs to be replaced every 3-5 years. A lithium-ion battery lasts 8-10 years or more. Let's look at a simple 10-year scenario. The lead-acid unit will require at least two expensive and disruptive battery replacements during that time. You have to pay for the new batteries, and you have to pay a technician to install them. The lithium-ion unit just works. You install it once and you are done. The initial "disadvantage" of a higher price turns into a major advantage of lower TCO and predictable budgeting. This eliminates the operational headache of tracking battery life and scheduling maintenance for dozens or hundreds of units across a facility. For a system integrator, proposing a lithium solution shows you're focused on long-term value for your client, not just the initial sale.
| Cost Factor over 10 Years | Typical Lead-Acid UPS | Daopulse Lithium-Ion UPS |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase Price | Lower | Higher |
| Battery Replacements | 2-3 Times | Zero |
| Maintenance Labor | High (Multiple Visits) | Zero |
| Total Cost of Ownership | HIGH | LOW |
What Is the Difference Between a Regular Battery and a Lithium Battery?
To most people, a battery is just a battery. It's a black box that stores power. This view misses the huge technological leap that lithium represents, affecting everything from size to performance.
The main differences are energy density, lifespan, and weight. A lithium battery stores much more energy in a smaller, lighter package and can be recharged thousands of times, far more than a "regular" lead-acid battery.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
When a client asks me this, I break it down into three simple points. First, energy density1. Think of a lead-acid battery as a heavy brick. A lithium battery with the same energy is the size of a small book. For our clients, this is huge. A 2U rackmount lithium UPS can provide the same backup time as a 4U lead-acid model. That saves incredibly valuable rack space in a data center. Second is lifespan2. A typical lead-acid battery can handle maybe 300-500 full charge cycles. Our LiFePO4 batteries are rated for over 2,000 cycles. It’s simply a more durable, long-lasting technology. Third is performance. A lead-acid battery’s voltage drops as it discharges, which can stress sensitive IT equipment. A lithium battery provides a very flat, stable voltage until it is nearly empty, providing cleaner and more reliable power to the connected load. These aren't just minor improvements; they represent a fundamental shift in what a battery can do.
Are Lithium Batteries Being Phased Out?
You read about new research into solid-state or other future battery technologies. This makes you wonder if you should wait, fearing that lithium-ion is about to become obsolete.
Absolutely not. Lithium-ion batteries are expanding into more applications than ever before. While new tech is always in development, lithium-ion is the mature, proven, and dominant high-performance solution for today and the foreseeable future.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
This is a concern I address by looking at the technology adoption lifecycle. New technologies like solid-state batteries are exciting, but they are still in the lab. They are years, maybe even a decade, away from being commercially available, affordable, and scalable for industrial applications like UPS systems. Think about it: global giants are investing billions to build lithium-ion battery factories right now. The entire electric vehicle industry is built on this technology. The application range of lithium batteries is constantly expanding into grid storage, medical devices, and critical data centers. You don't see this level of massive, global investment in a technology that is being phased out. For a procurement manager or system integrator planning a project today, lithium-ion is not a risky bet on the future. It is the established, reliable, and intelligent standard for high-performance power. It's the technology that will power your critical systems for the next decade.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries are a safe, long-lasting, and high-performance technology. Their higher initial cost is easily justified by a lower total cost of ownership, making them a wise investment.

