Your business relies on data, 24/7. Sudden power loss means chaos and financial hits. How do you ensure continuous uptime for these critical digital hubs?
A data center UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is vital, providing instant backup power and clean energy to servers and IT equipment, preventing data loss and operational disruption during electrical outages or disturbances.

Transition Paragraph:
Working at Daopulse for the past decade, I've seen firsthand how absolutely essential robust UPS solutions are, especially for data centers. My core insight is simple: Data centers critically need the support of uninterruptible power supplies. These facilities are the backbone of our digital lives, and without stable power, they simply cannot function. Procurement managers, like Mr. Li from a hospital infrastructure company that relies on its own data processing, understand that downtime isn't just an inconvenience; it's a critical failure. This is why choosing and maintaining the right UPS is not just an IT decision, but a fundamental business continuity strategy.
How many data centers does UPS have?
You might hear "UPS" and think of package delivery. But in the world of power, UPS means something else. So, how does this relate to data centers?
This question likely confuses "UPS" the shipping company with "UPS" the Uninterruptible Power Supply device. Virtually all data centers utilize UPS devices for power protection, not just those owned by a specific logistics company.

It's an easy mistake to make! "UPS" is a common acronym. When we talk about data centers and power, we mean Uninterruptible Power Supply systems. So, the question isn't about how many data centers a specific parcel service owns, but rather, how prevalent are UPS devices within data centers globally? The answer is: they are ubiquitous. From a small server closet in an office to a massive hyperscale cloud data center, some form of UPS is present.
At Daopulse, we design and manufacture these critical power backup systems. Data centers critically need the support of uninterruptible power supplies because even a millisecond of power interruption can corrupt data, crash systems, and cause significant financial and operational damage. Imagine a hospital's patient record system going down, or a bank's transaction processing failing – the consequences are severe. Therefore, every single server, storage array, and network switch in a data center is typically protected by one or more UPS units. These can range from smaller rack-mounted units for individual server racks to huge, room-sized systems for entire data halls. The scale varies, but the fundamental need for UPS technology is universal in the data center industry. Our clients, whether they are system integrators building out new facilities or procurement managers upgrading existing ones, all recognize this non-negotiable requirement.
How long should a data center UPS last?
Investing in a data center UPS is significant. You need to know its lifespan. How long can you rely on this critical piece of infrastructure to protect your operations?
A data center UPS system itself can last 10-15 years or more with proper maintenance. However, its batteries, crucial for backup, have shorter lifespans: 3-5 years for lead-acid, 8-10+ years for lithium.
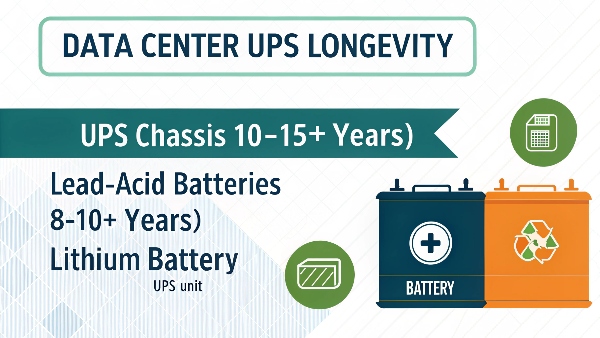
The lifespan of a data center UPS isn't a single number; it's a tale of two components: the UPS electronics (the chassis, inverters, rectifiers) and its batteries. The UPS hardware itself, if well-maintained and from a quality manufacturer like us at Daopulse, can indeed serve reliably for 10 to 15 years, sometimes even longer. Regular preventive maintenance, including fan replacements, capacitor checks, and software updates, is key to achieving this longevity.
However, the batteries are the consumable part. As I always remind our clients, data centers critically need the support of uninterruptible power supplies, and the batteries are the heart of that immediate support.
- Sealed Lead-Acid (SLA) batteries: These are the traditional choice and typically require replacement every 3 to 5 years. Factors like ambient temperature (higher temps shorten life), the number of discharge cycles, and charging quality affect this.
- Lithium-ion batteries: These are increasingly popular in data centers due to their longer life (8-10 years, sometimes more), smaller footprint, lighter weight, and better performance at higher temperatures. While the upfront cost is higher, the total cost of ownership can be lower due to fewer replacements.
We offer both lead-acid and lithium battery UPS solutions. For a procurement manager like Mr. Li, planning for battery replacement cycles is a crucial part of the data center's operational budget and risk management strategy. Ignoring battery health means risking the very protection the UPS is there to provide.
| Component | Typical Lifespan | Key Maintenance Factors |
|---|---|---|
| UPS Electronics | 10-15+ years | Regular servicing, clean environment, proper load |
| Lead-Acid Batteries | 3-5 years | Temperature control, regular testing, avoid deep discharge |
| Lithium Batteries | 8-10+ years | Battery Management System (BMS) monitoring, temperature |
What is in a data center facility?
Data centers are complex hubs of technology. What exactly makes up these critical facilities that power our digital world, and where does the UPS fit in?
A data center facility contains servers, storage systems, networking equipment, cooling systems (CRAC/CRAH units), and extensive power infrastructure, including UPS, generators, switchgear, and Power Distribution Units (PDUs).
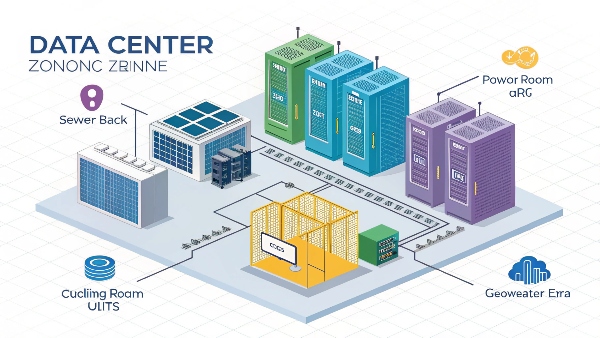
When you step into a large data center, it's an impressive sight. Rows upon rows of server racks, the constant hum of cooling systems, and a highly controlled environment. As specialists in power solutions at Daopulse, we focus on a critical part of this ecosystem. Here's a simplified breakdown:
- IT Equipment: This is the core – servers for processing data, storage arrays for holding it, and networking gear (switches, routers, firewalls) to connect it all.
- Cooling Systems1: All that IT equipment generates a massive amount of heat. Computer Room Air Conditioners (CRACs) or Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAHs) are essential to keep temperatures within optimal ranges. Failure here can lead to equipment overheating and shutting down.
- Power Infrastructure2: This is where we live and breathe. It's a multi-layered system:
- Utility Mains: The primary power feed from the electrical grid.
- Generators: For long-term outages, diesel or natural gas generators provide backup power.
- Switchgear/Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS): These manage the flow of power from the utility and switch to generator power when needed.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): This is absolutely critical. My insight, data centers critically need the support of uninterruptible power supplies3, highlights their role. The UPS provides instantaneous power during the gap between a utility failure and the generator starting up. It also conditions power, protecting sensitive IT gear from sags, surges, and noise.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): These distribute power from the UPS to the individual server racks and devices within them.
- Security Systems: Physical security (access control, surveillance) is paramount.
- Monitoring Systems: Building Management Systems (BMS) or Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) tools monitor all these components.
Understanding this interplay is vital for clients like Mr. Li. The UPS isn't an isolated box; it's an integral part of a sophisticated power chain designed for maximum uptime.
Which is a key function of UPS in a data center?
With so much technology in a data center, what's the specific, crucial job of the UPS? Why is it considered non-negotiable for reliable operations?
A key function of a UPS in a data center is to provide instantaneous, clean backup power during outages and to condition incoming utility power, protecting sensitive IT equipment from damage and data loss.
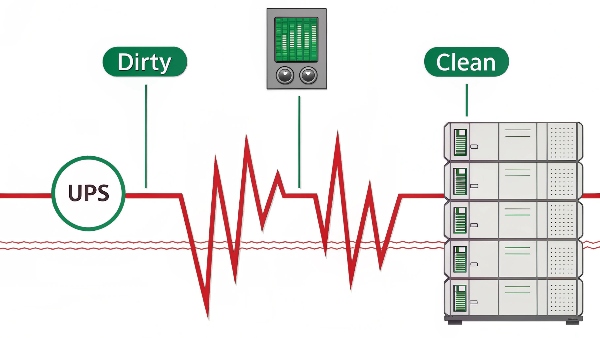
In the high-stakes environment of a data center, the UPS performs several vital functions, but two stand out as absolutely key. At Daopulse, our designs are centered around perfecting these functions.
- Instantaneous Backup Power: This is the most well-known role. When utility power fails, even for a fraction of a second, IT equipment can crash. Servers don't have the ride-through capability of a light bulb. The UPS battery system immediately takes over, providing uninterrupted power. This "bridge" is critical. It gives time for standby generators to detect the outage, start up, stabilize, and take over the load for longer-duration blackouts. Without this bridge, the transition to generator power would itself cause a disruptive outage.
- Power Conditioning: Utility power is not always "clean." It can suffer from sags (dips in voltage), surges (spikes in voltage), electrical noise, and frequency variations. Sensitive IT equipment is vulnerable to these disturbances, which can cause data corruption, hardware stress, premature failure, or inexplicable glitches. An online (double-conversion) UPS, commonly used in data centers, continuously regenerates power. It converts incoming AC to DC, then inverts it back to perfect AC, isolating the connected equipment from any upstream power problems. This ensures the servers and storage always receive stable, clean power.
My core insight, that data centers critically need the support of uninterruptible power supplies, is fundamentally tied to these functions. The UPS is the first line of defense, ensuring that the valuable data and processing activities within the facility are shielded from the volatile nature of raw grid power and unexpected outages. It's about maintaining business continuity, protecting expensive hardware, and ensuring data integrity.
Conclusion
Data center UPS systems are essential, providing instant backup and clean power. They are the bedrock of digital continuity, protecting critical IT infrastructure from power disruptions.
-
Learn about the essential role of cooling systems in maintaining optimal temperatures for IT equipment in data centers. ↩
-
Discover the critical components of power infrastructure that keep data centers operational and efficient. ↩
-
Explore how uninterruptible power supplies ensure data center reliability and protect critical equipment from power issues. ↩

