Downtime is the enemy, potentially costing businesses millions. How do data centers, the backbone of our digital world, achieve such impressive reliability and keep services running almost constantly?
Data centers ensure high uptime through redundant power and cooling systems (like N+1 or 2N), robust backup generators, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), multiple network connections, rigorous preventative maintenance, and sophisticated monitoring systems. These layers work together to prevent single points of failure.
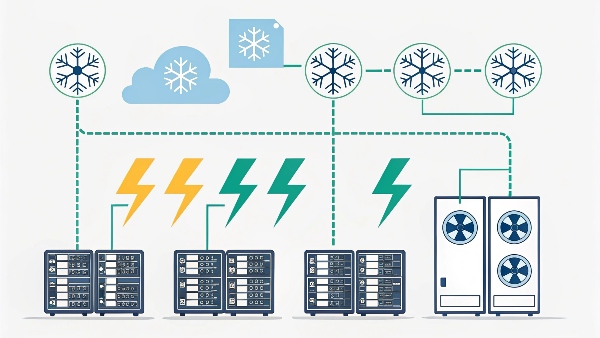
Transition Paragraph:
The seamless digital experiences we take for granted rely on these incredibly resilient facilities. At Daopulse, we've spent over a decade designing and manufacturing the OEM/ODM UPS systems that form a crucial part of this high-availability puzzle. My core insight is that data center infrastructure is critically important. The quality and design of every component, especially power, directly impact uptime. Let's explore the strategies and technologies data centers employ to maintain near-constant operation.
What is a Level 3 data center?
You hear terms like "Tier" or "Level" for data centers, but what does "Level 3" specifically mean for reliability? This classification can seem confusing, yet it's key to understanding a facility's capabilities.
A Level 3 (or more commonly, Tier 3) data center offers N+1 redundancy on critical systems. This means it has at least one backup for every essential component (power, cooling), allowing for maintenance or component failure without impacting IT operations. It guarantees 99.982% uptime.
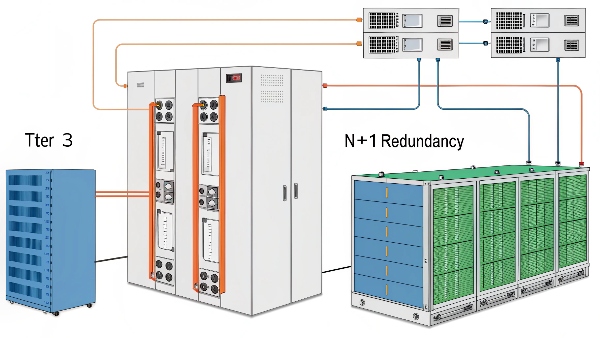
Dive deeper Paragraph:
The Uptime Institute's tier classification system is the global standard for data center reliability, though sometimes "Level" is used informally. A Tier 3 data center represents a significant step up in fault tolerance compared to Tier 1 or Tier 2 facilities. At Daopulse, many of our clients, especially those in finance or healthcare, require solutions like our modular UPS systems that can support Tier 3 or even Tier 4 designs. The defining characteristic of a Tier 3 facility is its "Concurrently Maintainable" infrastructure.
This means:
- N+1 Redundancy: For every component needed for ongoing operation (e.g., a UPS unit, a cooling unit, a generator), there is at least one independent backup. If one component fails or needs to be taken offline for planned maintenance, its backup seamlessly takes over.
- Multiple Distribution Paths: Tier 3 facilities typically have multiple independent power and cooling distribution paths. Not all paths need to be active simultaneously, but this design ensures that if one path is shut down (e.g., for repair or upgrade), another path can still deliver power and cooling to the IT equipment.
- No Shutdown for Maintenance: A key benefit is that individual pieces of equipment and distribution paths can be maintained, repaired, or replaced without requiring a shutdown of the critical IT load.
- Uptime Guarantee: Tier 3 data centers are designed for an availability of 99.982%, which translates to a maximum of 1.6 hours of downtime per year.
Compared to lower tiers:
- Tier 1 (Basic Capacity): Has single, non-redundant distribution paths and components. Any failure or planned maintenance will cause downtime. Offers around 99.671% uptime.
- Tier 2 (Redundant Components): Adds redundant capacity components (N+1 for power and cooling) but still has a single distribution path. Maintenance on the path still causes downtime. Offers around 99.741% uptime.
Choosing a Tier 3 facility means investing in a significantly higher level of reliability and fault tolerance. This is crucial for businesses where even brief outages can lead to substantial financial losses or reputational damage. Our role at Daopulse is to provide the robust, certified UPS systems that help achieve these demanding N+1 power redundancy goals.
| Tier Level | Key Characteristic | Redundancy | Annual Downtime (Approx.) | Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Basic Capacity | None (N) | 28.8 hours | Small businesses, non-critical applications |
| Tier 2 | Redundant Site Infrastructure | N+1 Components | 22 hours | Businesses needing some fault tolerance |
| Tier 3 | Concurrently Maintainable | N+1 Full | 1.6 hours | Most businesses, e-commerce, enterprises |
| Tier 4 | Fault Tolerant | 2N or 2N+1 | 26.3 minutes | Mission-critical, financial institutions |
Why should I go for Tier 3 data center?
Knowing a Tier 3 data center offers high uptime is one thing. But why should your business specifically choose this level, potentially at a higher cost? The benefits need to outweigh the investment.
You should go for a Tier 3 data center if your business operations are sensitive to downtime. The N+1 redundancy and concurrent maintainability significantly reduce outage risks, protecting revenue, reputation, and customer trust, making it ideal for most commercial and enterprise applications.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Deciding on the right data center tier is a critical business decision. For most organizations, particularly those with significant online operations, e-commerce platforms, or critical internal applications, a Tier 3 facility offers the best balance of reliability, performance, and cost. As a provider of essential UPS systems, Daopulse often sees firsthand the consequences when under-specced power infrastructure fails. The primary driver for choosing Tier 3 is risk mitigation.
Here's why it makes sense for many:
- Minimized Downtime: The 99.982% uptime (equating to just 1.6 hours of potential downtime per year) is a compelling figure. For businesses where every minute of outage translates to lost sales, customer dissatisfaction, or productivity hits, this level of availability is crucial.
- Concurrent Maintainability: The ability to perform maintenance or replace components without shutting down IT operations is a huge advantage. This means less disruption, no need for planned downtime windows for routine upkeep, and a more stable operational environment. Imagine needing to service a UPS unit; in a Tier 3 setup, the redundant unit takes over, and our Daopulse service team can work on the primary unit without affecting your servers.
- Protection Against Component Failure: With N+1 redundancy across power and cooling, the failure of a single UPS, generator, or air conditioning unit won't bring down your systems. This built-in resilience is a core value proposition.
- Business Continuity: Tier 3 facilities play a vital role in business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plans. They provide a stable and reliable environment for your critical IT assets.
- Improved ROI on IT Investment: Your expensive servers and software are only valuable when they are running. Investing in a Tier 3 data center helps ensure you get the maximum return on your IT hardware and software investments by keeping them operational.
While Tier 4 offers even higher fault tolerance (2N or 2N+1 redundancy, 99.995% uptime), it comes at a significantly higher cost and is typically reserved for organizations with extreme uptime requirements, like major financial exchanges or life-critical systems. For a Procurement Manager at a typical enterprise or a System Integrator designing solutions for commercial clients, Tier 3 often hits the sweet spot. The slightly higher cost compared to Tier 2 is usually justified by the vastly improved reliability and reduced risk profile. The data center infrastructure is critically important, and Tier 3 ensures this infrastructure is robust.
| Benefit of Tier 3 | Impact on Business Operations | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| High Availability | Near-continuous service, minimal unplanned outages. | Protects revenue, customer satisfaction, productivity. |
| Concurrent Maintainability | No need for downtime during scheduled maintenance or repairs. | Reduces disruptions, allows for proactive upkeep. |
| N+1 Redundancy | Resilience against single component failures in power/cooling. | Prevents system crashes due to equipment faults. |
| Enhanced Risk Management | Lower probability of costly downtime events. | Safeguards against financial and reputational damage. |
| Supports BCDR | Provides a stable foundation for disaster recovery plans. | Ensures business can recover quickly from incidents. |
What is data center hardware maintenance?
Data centers are packed with complex equipment running 24/7. What does it take to keep all this hardware in peak condition and prevent unexpected failures? It's more than just fixing things when they break.
Data center hardware maintenance involves proactive and reactive services to keep servers, storage, networking gear, and facility infrastructure (like UPS and cooling systems) operating reliably. It includes inspections, cleaning, parts replacement, firmware updates, and emergency repairs to maximize uptime and lifespan.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Data center hardware maintenance is a continuous, critical process. It's not just about reacting to failures; it's about proactively preventing them and ensuring all equipment operates at peak efficiency and reliability. At Daopulse, we emphasize the importance of regular maintenance for our UPS systems, as these are vital for protecting the IT hardware they support. Data center infrastructure is critically important, and its maintenance is a cornerstone of reliability.
Hardware maintenance encompasses several key areas:
- Preventative Maintenance (PM): This is scheduled, proactive work.
- Physical Inspections: Regularly checking for loose connections, signs of wear, overheating, or unusual noises.
- Cleaning: Removing dust and debris that can cause overheating or short circuits. This is especially important for air intakes on servers and cooling units.
- Component Health Checks: For UPS systems, this includes battery testing and proactive replacement before they fail. For servers, it might involve checking disk health (SMART status).
- Firmware/Software Updates: Applying patches and updates to hardware controllers, BIOS, and management interfaces to fix bugs and improve performance or security.
- Corrective Maintenance (CM): This is reactive, addressing issues as they arise.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnosing the root cause of a hardware failure.
- Parts Replacement: Swapping out failed components like hard drives, power supplies, fans, memory modules, or UPS batteries. Having readily available spares is crucial.
- Emergency Repairs: Addressing critical failures that impact service immediately.
- Predictive Maintenance: This uses data analytics and sensor information to predict when a component is likely to fail, allowing for replacement before an actual outage occurs. This is becoming more common with advanced monitoring tools.
Maintenance can be performed by in-house data center staff, the original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), or third-party maintenance (TPM) providers. Many data centers use a hybrid approach. For specialized equipment like large UPS systems, relying on the OEM (like Daopulse) or certified service partners is common, as they have the specific expertise and genuine parts. Effective hardware maintenance minimizes unexpected downtime, extends the lifespan of expensive equipment, and ensures the data center operates efficiently and safely. This directly supports the goal of high availability.
| Maintenance Type | Activity Examples | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Preventative | Regular inspections, cleaning, battery tests, firmware updates. | Prevent failures, optimize performance, extend equipment life. |
| Corrective | Replacing failed hard drive, fixing a faulty power supply unit. | Restore functionality after a failure, minimize downtime. |
| Predictive | Analyzing sensor data to anticipate disk failure, replacing early. | Avoid unplanned outages, optimize maintenance schedules. |
| Condition-Based | Monitoring vibration on a fan motor, servicing when thresholds met. | Perform maintenance only when needed, based on actual condition. |
What is the cost of setting up an AWS data center?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) runs a massive global network of data centers. What kind of investment does it take to build one of these hyperscale facilities? The numbers are undoubtedly staggering.
The cost of setting up an AWS data center is immense, typically ranging from hundreds of millions to over a billion US dollars per facility. This includes land, construction, extensive power and cooling infrastructure, servers, networking gear, and high security.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Building a data center on the scale that AWS operates is an undertaking of monumental financial and logistical complexity. While AWS doesn't publicly disclose exact costs for individual facilities, industry estimates and publicly available information about similar hyperscale projects suggest figures easily reaching into the hundreds of millions, and often exceeding a billion dollars, for a single, large data center campus. At Daopulse, while we supply UPS solutions to various types of data centers, the sheer scale of power infrastructure required by AWS is on another level. Data center infrastructure is critically important, and for AWS, it's built for hyper-efficiency and massive scalability.
Several factors contribute to these enormous costs:
- Land Acquisition & Preparation1: Hyperscale data centers require large tracts of land, often in strategic locations with access to massive power and fiber optic networks.
- Building Construction: These are not ordinary buildings. They are highly specialized structures designed for security, heavy floor loads, and optimized airflow.
- Power Infrastructure2: This is a huge expense. It involves redundant high-voltage connections to the grid, massive arrays of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), fleets of large backup generators (often diesel), and complex power distribution systems. AWS custom-designs much of its own power equipment, including UPS systems, to maximize efficiency at scale.
- Cooling Systems3: Removing the heat generated by tens of thousands of servers requires sophisticated and large-scale cooling plants, including chillers, air handlers, and often innovative water-saving or free cooling techniques.
- IT Hardware: The cost of servers, storage arrays, and high-speed networking equipment (routers, switches) runs into many millions of dollars per facility. AWS benefits from economies of scale by designing and often manufacturing its own server and networking hardware.
- Security: Comprehensive physical and cybersecurity measures, including perimeter security, access control, surveillance, and advanced threat detection systems, add significantly to the cost.
- Networking: Building out robust, redundant fiber optic connectivity, both internally and to external internet peering points, is a major investment.
AWS typically builds "Availability Zones," which consist of one or more discrete data centers, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity, housed in separate facilities. This architecture provides resilience. The sheer scale and the custom-designed nature of much of their infrastructure contribute to these high setup costs. However, this massive investment allows them to offer highly reliable and scalable cloud services globally.
| Cost Component | Description | Scale for AWS-type Facility |
|---|---|---|
| Land & Site Prep | Acquiring and preparing suitable land. | Many acres, often strategically located |
| Building Shell | Construction of the physical data center buildings. | Hundreds of thousands of square feet |
| Power Systems | Utility feeds, UPS, generators, switchgear, PDUs. | Many Megawatts (MW) capacity |
| Cooling Systems | Chillers, CRAC/CRAH units, cooling towers, pipework. | Matched to power capacity, very large |
| IT Hardware | Servers, storage, networking equipment. | Tens of thousands of custom units |
| Security Systems | Physical access controls, surveillance, cyber defenses. | Multi-layered, sophisticated |
| Network Connectivity | Fiber optic cabling, routers, peering arrangements. | High-bandwidth, multiple providers |
Conclusion
Data centers achieve high uptime through meticulous design focusing on redundancy in power, cooling, and networking. Tier 3 standards ensure this, supported by diligent hardware maintenance for long-term, reliable operations.
-
Understanding land acquisition strategies can help optimize site selection for data centers, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness. ↩
-
Exploring power infrastructure insights can reveal how to manage energy costs and improve operational efficiency in data centers. ↩
-
Learning about advanced cooling techniques can enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs in large-scale data centers. ↩

