Ever driven past a large, plain building with no windows and wondered what's inside? Many of these are data centers, the hidden engines of our digital lives. Understanding how to spot them can be tricky.
You can often identify data center buildings by their lack of windows, numerous large cooling units (HVACs, chillers) on the roof or sides, high-security fences and cameras, and prominent backup power generators.

Transition Paragraph:
These seemingly anonymous structures are the nerve centers of the internet. At Daopulse, we've supplied critical power solutions to these facilities for over a decade. My key insight is that data centers have high power demands, and if the power is unstable, it will cause significant losses. This understanding of their vulnerability to power issues shapes how we design our UPS systems. So, let's delve into the tell-tale signs that help you spot these vital technological hubs and understand more about their intricate operations.
Can Google Data Center be powered solely by solar energy?
Google aims for 100% renewable energy. But can its massive data centers truly run only on sunshine, 24/7? This raises questions about the feasibility of greening such power-hungry operations.
No, a Google Data Center cannot currently be powered solely by solar energy around the clock. Solar power is intermittent, while data centers need constant, reliable electricity. Google uses a mix of renewables, including solar, and grid power, aiming to match 100% of its annual consumption with renewable energy purchases.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Google's commitment to 100% renewable energy is a significant goal. However, powering a massive data center complex exclusively with direct solar energy, day and night, presents major hurdles. The core issue is that solar panels only generate electricity when the sun is shining. Data centers, on the other hand, demand a continuous, uninterrupted power supply, 24/7, 365 days a year. My experience at Daopulse supplying UPS systems confirms that even facilities with significant renewable generation still rely heavily on grid power and robust backup, like our lead-acid and lithium battery UPS solutions, to bridge any gaps.
Google's strategy involves matching its total annual electricity consumption with purchases of renewable energy from sources like wind and solar farms through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). This means that while a specific data center might be drawing power from the local grid (which could be from mixed sources), Google ensures that an equivalent amount of renewable energy is added to the grid elsewhere.
Key challenges for 100% direct solar power include:
- Intermittency: Solar power is unavailable at night or during heavily overcast days.
- Energy Storage: Storing enough solar energy in batteries to power a data center through the night and cloudy periods would require an immense, costly battery infrastructure.
- Land Footprint: The sheer area required for solar panels to generate enough power for a large data center would be vast.
So, while solar is a vital part of Google's (and the industry's) green energy strategy, it's currently one component of a broader portfolio that includes grid power, other renewables, and sophisticated energy management. The critical need for constant power means our certified UPS systems remain essential.
| Aspect | Pros for Data Centers (with Solar) | Cons for Data Centers (Solely Solar) |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Reduced carbon footprint | Intermittent supply, high land use for 100% coverage |
| Cost | Lower long-term energy costs (with PPAs) | Very high upfront cost for 100% solar + massive storage |
| Reliability | Contributes to renewable energy mix | Not directly reliable 24/7 without massive storage/grid |
| Operations | Supports corporate sustainability goals | Complex energy management, reliance on grid balancing |
What is it called when you work at a data center?
"Working at a data center" seems straightforward. But what are the actual job titles and roles inside these complex facilities? This lack of clarity can hide the diverse career opportunities available.
People working at a data center hold various specialized roles. Common titles include Data Center Technician, Facility Engineer, Network Engineer, Systems Administrator, Security Officer, and Operations Manager, reflecting the wide range of skills needed to keep these critical facilities running.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
The term "data center worker" doesn't quite capture the variety of specialized roles involved in keeping these intricate facilities operational. Having supplied UPS systems to countless data centers through Daopulse, I've interacted with professionals in many different capacities. Each role is crucial for the data center's smooth functioning.
Here are some common positions:
- Data Center Technician: These are the hands-on experts. They install, maintain, and troubleshoot servers, storage devices, and network equipment. They manage cabling and respond to hardware issues. This is often an entry-level position offering great learning opportunities.
- Facility Engineer/Manager: These professionals are responsible for the physical plant – power, cooling, fire suppression, and building security. They ensure systems like our UPS units, generators, and HVAC systems are always working optimally. Their expertise is vital for uptime.
- Network Engineer: They design, implement, and manage the complex network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and firewalls, ensuring data flows efficiently and securely.
- Systems Administrator/Engineer: They manage the servers' operating systems, software applications, and storage solutions. They ensure systems are patched, backed up, and performing well.
- Security Personnel: This includes physical security guards who control access and monitor surveillance, as well as cybersecurity analysts who protect against digital threats.
- Operations Manager: This role oversees the day-to-day running of the data center, managing staff, coordinating maintenance, and ensuring adherence to service level agreements.
The common thread is a need for technical aptitude, meticulous attention to detail, and strong problem-solving skills. As data centers grow in complexity, the demand for skilled professionals in these roles continues to rise.
| Role Category | Example Titles | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Operations & Tech | Data Center Technician, Smart Hands Tech | Hardware installation, troubleshooting, cabling, remote support |
| Facilities | Facility Engineer, Critical Facility Manager | Power systems (UPS, generators), cooling, building systems |
| Networking | Network Engineer, Network Architect | Router/switch configuration, network design, traffic management |
| IT Systems | Systems Administrator, Storage Engineer | Server OS, virtualization, storage area networks, backups |
| Security | Security Officer, Cybersecurity Specialist | Physical access control, surveillance, threat detection |
| Management | Data Center Manager, Site Operations Lead | Team supervision, process improvement, vendor relations |
What is data center?
We hear "data center" often, but what does it truly mean? It's more than just a building filled with computers. Misunderstanding its core function obscures its profound impact on our digital society.
A data center is a secure, specialized facility. It houses IT infrastructure like servers, data storage systems, and networking equipment. Its purpose is to collect, store, process, distribute, or allow access to large amounts of data and applications.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
At its heart, a data center is the physical home for the digital world. It's a purpose-built facility designed to support the IT infrastructure that powers so much of our modern lives – from streaming movies and online shopping to complex financial transactions and scientific research. My work at Daopulse involves ensuring these facilities have absolutely reliable power through our OEM/ODM UPS systems, because any interruption can have far-reaching consequences.
The core components of a data center include:
- IT Equipment: This is the "payload" – servers for computation, storage arrays for holding data, and networking gear (switches, routers, firewalls) to connect everything and provide access.
- Power Infrastructure1: This is critical. It includes utility power feeds (often redundant), massive uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) like our lead-acid or high-efficiency lithium battery solutions, backup generators for extended outages, and power distribution units (PDUs) to deliver power to the racks.
- Cooling Systems2: IT equipment generates a lot of heat. Sophisticated cooling systems (CRACs, CRAHs, chillers, etc.) are essential to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
- Security Systems3: Both physical security (access control, surveillance) and cybersecurity measures protect the valuable equipment and data.
- The Building: A robust structure designed to house all these systems securely and efficiently.
Data centers can be privately owned by a single company (enterprise data centers), or they can be colocation facilities where multiple tenants rent space and power. Hyperscale data centers, run by giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft, are massive operations supporting cloud services. Regardless of size or type, their function is vital.
| Data Center Component | Primary Function | Why It's Critical for Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Servers | Execute software, process data, host applications | The computational engine |
| Storage Systems | Persistently store and retrieve vast amounts of digital data | The memory and archives |
| Networking Equipment | Interconnect IT systems and connect to external networks | The communication pathways |
| Power Infrastructure | Provide continuous, clean, and redundant electrical power | Prevents downtime, data loss, equipment damage |
| Cooling Systems | Remove heat generated by IT equipment, control humidity | Ensures equipment reliability and longevity |
| Building & Security | House and protect all systems and data | Physical integrity and defense against threats |
How to build a data centre in India from scratch?
Building a data center in a dynamic market like India seems complex. Where does one even start such a massive undertaking? Understanding the unique local factors is key to navigating this process.
Building a data center in India from scratch involves careful site selection (considering power, fiber, and risks), navigating complex regulations, designing for India's diverse climate, ensuring highly reliable power and cooling infrastructure, and meticulous project management.
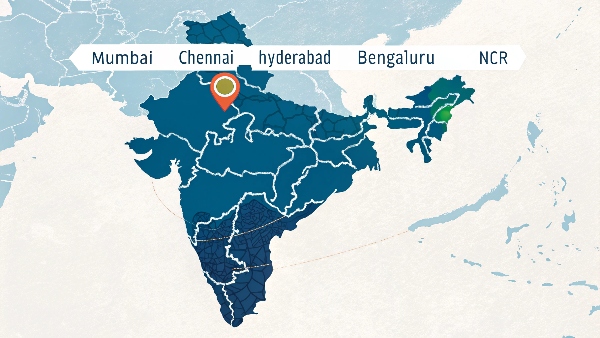
Dive deeper Paragraph:
India's digital economy is booming, creating a massive demand for data center capacity. Building one from scratch there is a significant undertaking but also a great opportunity. From my perspective at Daopulse, where we provide globally certified (CE, RoHS, ISO) UPS solutions, ensuring robust power infrastructure is a top priority, especially given India's varied power grid stability. Data centers have high power demands, and if the power is unstable, it will cause significant losses – this is a crucial consideration anywhere, but especially important in rapidly developing power landscapes.
Key steps and considerations include:
- Strategic Site Selection: This is paramount. You need proximity to reliable power substations (preferably with multiple feeds), robust fiber optic connectivity from multiple carriers, low risk of natural disasters (flooding, earthquakes), and accessibility for logistics and talent. Major hubs include Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and the NCR.
- Navigating Regulations: India has a multi-layered regulatory environment. This involves national, state, and local permits for construction, environmental clearances, and data-related laws (like data localization, if applicable).
- Power Infrastructure Design: Given the potential for grid fluctuations in some areas, a highly resilient power system is non-negotiable. This means high-capacity, redundant UPS systems (like our lead-acid or advanced lithium battery solutions), multiple backup generators, and efficient power distribution.
- Climate-Specific Cooling: Much of India experiences high ambient temperatures and humidity. Cooling systems must be designed for efficiency and resilience in these conditions, often incorporating solutions like free cooling or liquid cooling where appropriate.
- Supply Chain & Logistics: Sourcing specialized equipment and managing the supply chain can be complex. Working with experienced local partners is often beneficial.
- Skilled Workforce: Access to trained engineers and technicians for construction and ongoing operations is essential.
The Indian government is actively promoting data center development through various policies and incentives. However, thorough due diligence and robust planning are critical for success.
| Phase of Building in India | Key Considerations & Actions | Specific Challenges/Opportunities in India |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Planning & Feasibility | Market analysis, site selection, initial design, budget, permits. | Land acquisition, power availability assessment, regulatory approvals. |
| 2. Design & Engineering | Detailed power, cooling, security, and network design. | Designing for high heat/humidity, ensuring modular scalability. |
| 3. Procurement & Construction | Sourcing equipment (UPS, chillers, etc.), building work. | Import logistics, finding skilled contractors, monsoon season impact. |
| 4. Commissioning | Integrating and testing all systems (IST). | Ensuring systems perform to spec under local conditions. |
| 5. Operation & Maintenance | Staffing, monitoring, preventative maintenance, compliance. | Retaining skilled talent, managing operational energy costs. |
Conclusion
Identifying data centers involves spotting key architectural and infrastructure clues. From Google's green energy goals to the complexities of building in India, understanding these facilities reveals their critical role in our world.
-
Understanding Power Infrastructure is crucial for ensuring data center reliability and efficiency. Explore this link to learn more. ↩
-
Cooling Systems are vital for preventing overheating in data centers. Discover how they function to maintain optimal temperatures. ↩
-
Security Systems are essential for protecting data and equipment. Learn about the various measures in place to safeguard data centers. ↩

