Many of us charge our devices overnight out of convenience, but is this practice actually safe for lithium-ion batteries?
Modern lithium-ion batteries with proper Battery Management Systems (BMS) can safely remain on chargers overnight. The BMS automatically stops charging when full, preventing overcharge damage. However, prolonged 100% charge can slightly reduce long-term battery health.
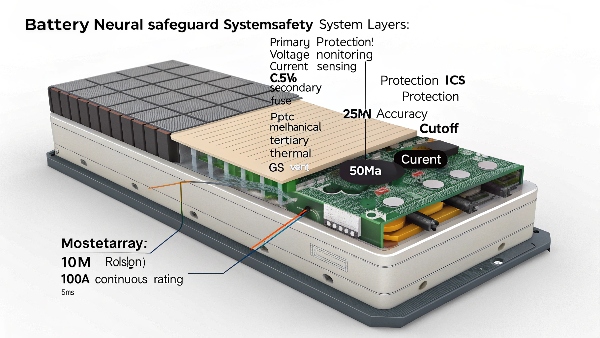
Through years of battery manufacturing, we've found that occasional overnight charging won't cause immediate damage, but making it a regular habit might shorten overall lifespan by keeping cells at peak voltage too long.
Can You Fast Charge a Lithium-Ion Battery?
In our fast-paced world, who has time to wait for a slow charge? But is pushing charging speed limits really good for your battery?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries can safely fast charge within manufacturer specifications (typically 0.5C-1C rates), but consistent fast charging generates more heat and may reduce overall cycle life by 10-20% compared to standard charging.
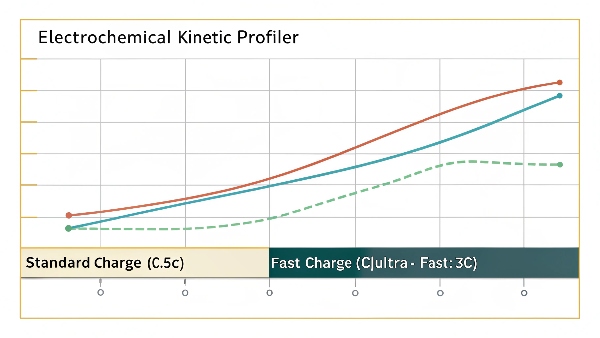
Fast Charging Guidelines:
| Charge Rate | Example (for 3000mAh battery) | Typical Use Case | Expected Lifespan Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5C | 1.5A current | Everyday charging | Baseline (500-1000 cycles) |
| 1C | 3A current | Quick top-ups | 10-15% reduction |
| 2C | 6A current (if supported) | Emergency use | 20-30% reduction |
Important notes from our testing:
- Heat is the enemy - Fast charging creates more heat
- Cool batteries charge faster - Avoid fast charging hot batteries
- Not all batteries support fast charging - Check manufacturer specs
What Are the Negatives of Fast Charging?
While fast charging offers convenience, understanding its drawbacks helps make informed charging decisions.
The main negatives of fast charging include increased heat generation, potential long-term capacity loss, higher component stress, and possible safety risks if proper cooling isn't maintained during rapid charging.
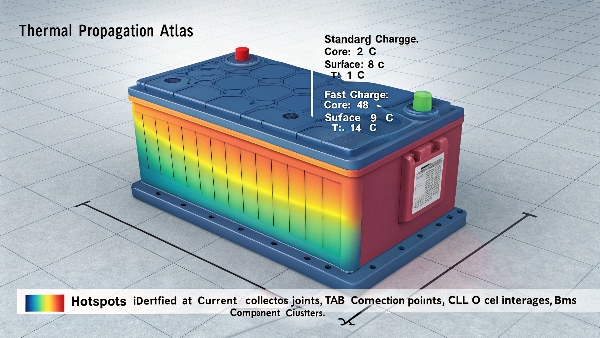
Fast Charging Disadvantages:
-
Heat-Related Issues
- Accelerated chemical degradation
- Potential electrolyte breakdown
- Increased risk of thermal runaway
-
Physical Stress
- Expanded-contracted electrodes
- Higher current demands on BMS
- Increased wear on charging components
-
Performance Impact
- Possible temporary capacity reduction
- More frequent capacity calibration needed
- Voltage fluctuations during charging
Our quality control department tracks 20% more warranty claims on batteries regularly fast-charged at maximum rates.
What Is the 80 20 Rule for Lithium Batteries?
Extending battery life often comes down to simple charging habits you can start today.
The 80-20 rule recommends keeping lithium-ion batteries between 20% and 80% charge for daily use to maximize lifespan. Completely draining or keeping fully charged constantly causes more stress on battery chemistry.
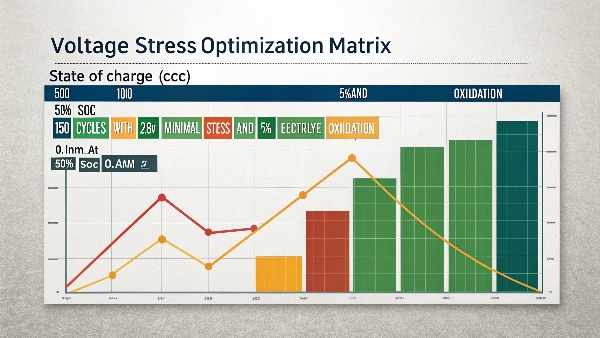
Implementing the 80-20 Rule:
| Practice | Benefit | Expected Lifespan Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Avoiding 100% charges | Reduces voltage stress | +15-20% more cycles |
| Stopping at 80% | Less electrode expansion | +10-15% capacity retention |
| Charging at 20% | Prevents deep discharge | +20-25% cycle life |
Our long-term tests show:
- Batteries kept at 30-70% last longest
- Occasional full charges are okay (once a month)
- Storage at 50% is ideal for unused batteries
How Fast Can Lithium Batteries Be Charged?
Pushing charging limits requires understanding battery engineering constraints.
Most lithium-ion batteries can safely charge at 0.5C-1C rates (1-2 hours), with advanced batteries supporting up to 3C (20 minute) charging with special cooling systems. Charging speed depends on battery chemistry and design.
Maximum Safe Charging Rates:
| Battery Type | Normal Charge Rate | Maximum Safe Rate | Special Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Li-ion | 0.5C (2 hours) | 1C (1 hour) | Passive cooling |
| LiFePO4 | 0.5C | 1C | None |
| Advanced Fast-Charge | 1C | 3C (20 minutes) | Active cooling |
| EV Batteries | 0.3C | 2-3C | Liquid cooling |
Key observations from our production line:
- Thinner electrodes1 enable faster charging
- Higher grade materials handle more current
- Advanced BMS2 is crucial for fast charging safety
- Cooling systems become essential above 1C rates

