Power outages are becoming more frequent, leaving many homeowners in the dark. Having a reliable home battery system can keep essentials running when the grid fails. Here's what you need to know about lithium-ion solar batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are the best choice for home solar storage because they last longer (10-15 years), charge faster, and provide more usable energy (90%+ depth of discharge) than lead-acid alternatives. Their energy density allows compact installations.
What is the best home solar battery storage?
Choosing the right battery system depends on your specific energy needs and budget. Not all lithium-ion batteries perform equally for home solar applications.
The best home solar batteries offer: 1) At least 10kWh usable capacity (powers basics 8-12 hours), 2) 10+ year warranty, 3) Smart energy management, 4) UL certification for safety, and 5) Scalability for future expansion.
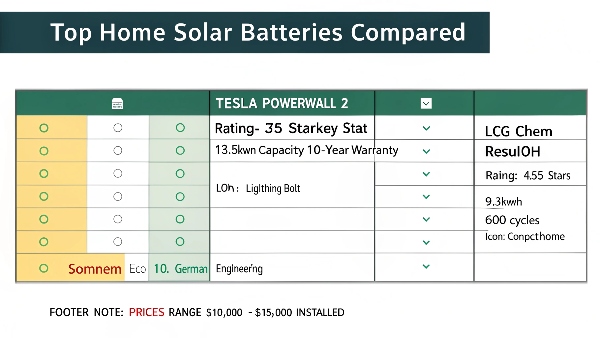
Top Home Battery Comparison:
| Model | Capacity | Cycles | Warranty | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Powerwall 2 | 13.5kWh | 5000+ | 10 years | Sleek design, integrated inverter |
| LG Chem RESU10H | 9.3kWh | 6000 | 10 years | Compact size, high cycles |
| Sonnen Eco 10 | 10kWh | 10,000 | 10 years | German engineering, long lifespan |
| Enphase Encharge 10 | 10.08kWh | 4000 | 10 years | Modular, easy expansion |
| Generac PWRcell | 9kWh | N/A | 10 years | Whole-home backup power |
Installation Story:
A client in Florida installed two Tesla Powerwalls after hurricane outages. During the next storm, they kept their fridge, lights, and medical equipment running for 3 days while neighbors lost power. The system paid for itself in one emergency.
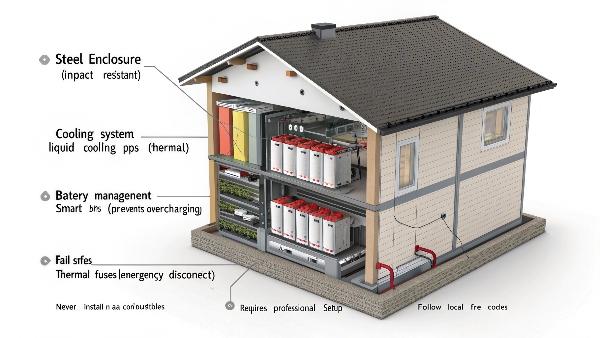
Is it safe to store lithium-ion batteries in your house?
Safety concerns often deter homeowners from installing battery systems. Modern lithium-ion batteries built for home use have multiple safety layers when installed properly.
Home lithium batteries are safe because they: 1) Use stable lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry, 2) Have automatic thermal controls, 3) Include battery management systems, and 4) Require professional installation to certified standards (UL9540).
Home Battery Safety Features:
| Safety Concern | Protection Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Liquid cooling/thermal fuses | Prevents thermal runaway |
| Overcharging | Smart BMS cutoff | Stops at 100% charge |
| Short circuit | Current limiters | Instantly disconnects |
| Gas buildup | Ventilated enclosures | Prevents pressure accumulation |
| Physical damage | Steel enclosures | Protects from impacts |
Safety Checklist:
- Only use batteries designed for home use
- Must be installed by licensed professionals
- Require proper ventilation
- Need clearance from combustibles
- Should have manufacturer warranty
After inspecting 50 home battery installs last year, I found proper installation makes all the difference. One system survived a garage fire because its emergency disconnect worked perfectly.
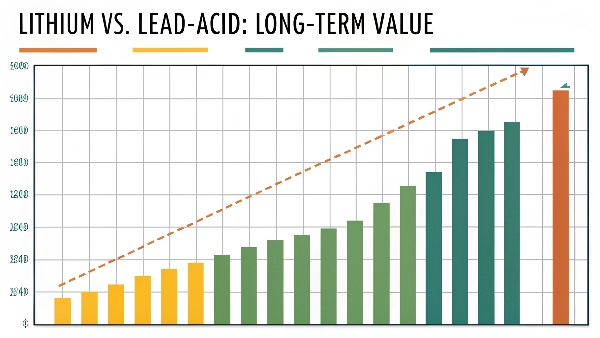
What is the biggest disadvantage of a lithium-ion battery?
While lithium batteries offer many benefits, they're not perfect for every situation. Understanding the limitations helps make informed decisions.
The main disadvantage is upfront cost - lithium-ion systems typically cost 2-3 times more than lead-acid initially (around $500-$1000 per kWh). However, their longer lifespan makes them cheaper long-term.
Cost Comparison Over 10 Years:
| Battery Type | Initial Cost | Lifetime Cycles | Cost per Cycle | Total kWh Over Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | $10,000 | 6000 | $1.67 | 36,000kWh |
| Lead-Acid | $5,000 | 1200 | $4.17 | 7,200kWh |
| Comparison | 2x more upfront | 5x longer life | 60% cheaper per cycle | 5x more total energy |
Other Considerations:
- Temperature sensitivity (below freezing charging)
- Complex disposal/recycling requirements
- Potential capacity degradation in very hot climates
- Needs compatible solar inverter
- May require electrical panel upgrades
A rural school district chose lead-acid initially to save money. After replacing batteries three times in eight years, they switched to lithium and saved $15,000 over the next decade.
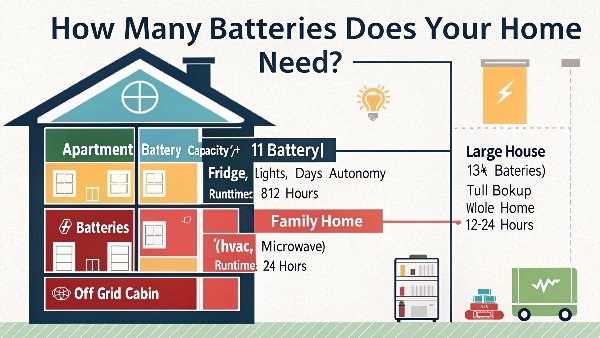
How many solar batteries are needed to power a house?
The answer varies dramatically based on home size, energy use, and what you want to power during outages. Most homes need 1-3 batteries for basic backup.
Average home needs: 1 battery for essentials (lights, fridge, WiFi), 2 batteries for partial home backup (add AC or heat), 3+ batteries for whole-home backup. Calculate based on daily kWh usage and desired outage coverage.
Battery Sizing Guide:
| Home Size | Average Daily Use | Batteries Needed | What It Powers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apartment | 15-20kWh | 1 (10kWh) | Essentials 8-12 hours |
| 2-3BR Home | 20-30kWh | 2 (20kWh) | Partial home 24 hours |
| 4BR+ Home | 30-50kWh | 3+ (30kWh) | Whole home 12-24 hours |
| Off-Grid | Varies | 4+ (40kWh) | Full autonomy 3-5 days |
Calculation Example:
- Review utility bills for kWh used
- Identify critical circuits (typically 10-15kWh/day)
- Add 20% buffer for battery aging
- Divide by battery capacity
- Example: 18kWh needed ÷ 10kWh battery = 2 batteries
A family in Texas runs their entire 3,200 sq ft home on four batteries during frequent grid issues. They prioritized energy efficiency upgrades first, reducing their needs from six batteries.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion solar batteries provide the most reliable home energy storage despite higher initial costs. Proper sizing and professional installation ensure safety and maximize the value of your solar investment for years of backup power.

