Power outages happen. Your UPS suddenly shuts off. You lose critical data or medical equipment fails. This could mean an overloaded UPS. Let me explain why this happens and how to prevent it.
A UPS overloads when connected devices draw more power than its capacity. Main causes include: plugging in too many devices, high startup power surges, incorrect UPS sizing, old batteries, faulty wiring, or adding new equipment without checking power needs.

Understanding overload is just the start. Many critical applications like hospitals need reliable backups. Let's look at solutions for these special cases.
What can I get to provide a battery backup for a hospital bed?
Imagine a power failure during surgery. Medical devices stop. Lives are at risk. Hospital beds need special UPS solutions that standard units can't provide.
Choose a medical-grade UPS with: pure sine wave output, isolated power circuits, long battery runtime (4+ hours), silent operation, IEC 60601 certification, and rack-mount design for space-saving under beds.
Critical features for hospital UPS:
Patient safety comes first. These UPS systems have special protections normal ones lack:
- Isolated Power - Prevents electrical interference between devices
- Pure Sine Wave - Safe for sensitive medical equipment
- Automatic Self-test - Checks battery health daily
- Hot-swap Batteries - Change batteries without shutting down
- Alarm System - Notifies staff of any issues
| Battery Type Comparison | Feature | Lead-Acid | Lithium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 2-3 years | 5-7 years | |
| Charge Time | 8 hours | 2-3 hours | |
| Weight | Heavy | Light | |
| Cost | $ | $$ |
Our medical UPS units helped a children's hospital in Tokyo maintain power during a 3-hour blackout last year. All life support systems stayed online. That's why we recommend lithium batteries - they last longer and charge faster, though they cost more upfront.

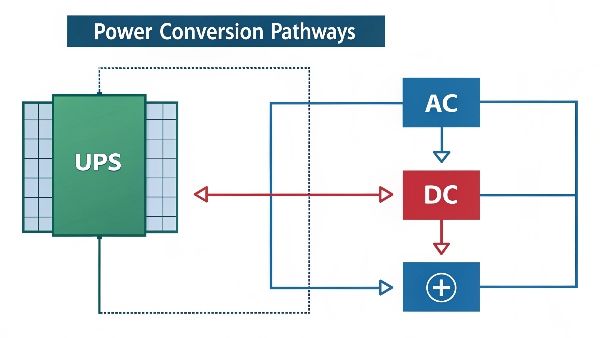
AC/DC UPS category
Ever wonder why some UPS systems look different? That's because they handle different power types. Choosing wrong could damage your expensive equipment.
AC UPS systems power standard 120V/230V devices (computers, lights). DC UPS systems power specialized 12V/24V/48V equipment (telecom towers, solar systems). Some hybrid UPS handle both types in one unit.
When to use each type:
Location matters more than you think:
- Offices/Hospitals → AC UPS (standard wall power)
- Cell Towers → DC UPS (48V equipment)
- Boats/RVs → DC UPS (12V/24V systems)
- Solar Installations → Hybrid AC/DC UPS
| Power Conversion Efficiency | System Type | Efficiency | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC UPS | 85-90% | Buildings | |
| DC UPS | 92-95% | Telecom | |
| Hybrid | 88-93% | Solar farms |
We designed a hybrid UPS for a remote clinic in Alaska. It handles their solar panels (DC) and medical equipment (AC) simultaneously. Remember: Always match the UPS to your equipment's power requirements. Check voltage labels twice before buying.
Doctors save lives daily but many don't understand their UPS systems. This lack of knowledge can be dangerous when power fails.
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is an intelligent battery backup that: 1) Provides instant power during outages, 2) Protects against voltage spikes, 3) Gives time to safely shut down equipment or switch to generators.
Why hospitals need special UPS:
- Zero Transfer Time1 - Life support can't blink
- Clean Power2 - Medical imaging needs stable voltage
- Long Runtime - Must last until generator starts
- Remote Monitoring3 - Staff can check status anywhere
Common Mistakes in Hospitals:
- Using office UPS for medical devices
- Not testing batteries monthly
- Overloading circuits
- Ignoring alarm warnings
A London hospital avoided disaster last winter when their MRI UPS automatically engaged during a blackout. The $2 million machine was scanning a patient's brain. Without proper UPS, they would have lost critical scan data mid-procedure. Always size your UPS at least 25% larger than needed for safety margins.
What is inverter and ups?
Many confuse UPS with inverters. This mistake can cost thousands when equipment fails. Understand the key differences to protect what matters.
UPS provides instant backup (milliseconds), protects against power fluctuations, and is for critical loads. Inverters have delays (seconds), no power protection, and are for non-critical loads like lights.
Critical differences:
| Feature | UPS | Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Switch Time | 2-8 milliseconds | 0.5-5 seconds |
| Protection | Full power filtering | None |
| Cost | $$$ | $ |
| Best Use | Medical equipment | Home appliances |
| Battery Life | 3-5 years | 1-2 years |
We helped convert a dialysis center from inverters to medical UPS last year. Before, power blips would reboot machines mid-treatment - dangerous for patients. Now they have seamless power. Remember: For anything life-critical, only use UPS. For lights or fans, inverters work fine.

Conclusion
Prevent UPS overload through proper sizing and regular maintenance. Choose medical-grade UPS for critical care. Understand AC/DC types and never confuse UPS with inverters.
-
Understanding Zero Transfer Time is crucial for ensuring life support systems remain operational without interruption. Explore this link to learn more. ↩
-
Clean Power is essential for accurate medical imaging. Discover how it impacts patient care and technology reliability by exploring this resource. ↩
-
Remote Monitoring enhances the efficiency of UPS systems in hospitals, ensuring staff can manage power needs effectively. Check out this link for insights. ↩

