Imagine losing critical work or a game due to a sudden power outage. These power disruptions are frustrating and can even damage your expensive electronics.
UPS systems, or Uninterruptible Power Supplies, are devices that provide emergency power to your electronics when the main power source fails. They protect against outages, surges, and other power problems, ensuring continuous operation and data safety.

Working at DAOPULSE for the past 10 years, I've seen firsthand how essential these systems are. We're an OEM/ODM manufacturer, and we create UPS solutions for global brands, wholesalers, and retailers. Many people think a UPS is just a big battery, but it's more complex. It's a safeguard for your valuable equipment. The core idea is simple: keep things running smoothly, even when the power company can't. This guide will help you understand what these systems are and why they matter so much.
What are the three types of UPS systems?
You know you need a UPS, but the terms "standby," "line-interactive," and "online" are confusing. Choosing the wrong one means you might not get the protection your equipment really needs.
The three main types of UPS systems are Standby (Offline), Line-Interactive, and Online (Double-Conversion). Each offers different levels of protection and features, suiting various needs and budgets.
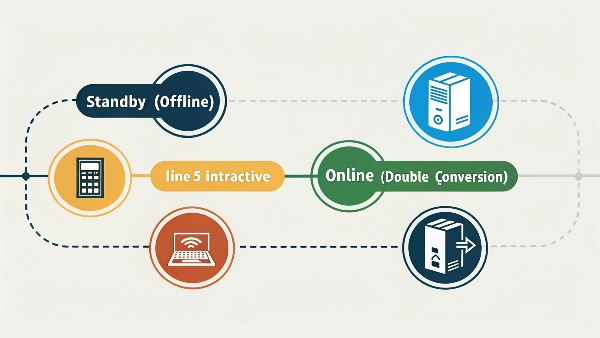
Understanding these three types is key to picking the right UPS. Let me break them down for you.
First, there's the Standby UPS, sometimes called an Offline UPS. This is the most basic type. It monitors the incoming power. If it detects a problem like an outage or a big surge, it quickly switches to its battery. It's generally the most affordable. It's good for home computers or less critical equipment.
Next is the Line-Interactive UPS. This is a very popular choice and one we frequently design at DAOPULSE , including both our lead-acid and lithium battery UPS solutions. It does more than just switch to battery. It has an autotransformer that corrects small power fluctuations – like sags (brownouts) or swells (surges) – without using the battery. This saves battery life and gives better protection than a standby UPS. It's great for small office servers, network equipment, and higher-end home PCs.
Finally, there's the Online UPS, also known as a Double-Conversion UPS. This type provides the highest level of protection. The connected equipment always runs off the UPS's inverter, which constantly rebuilds clean, stable power from the battery system. The incoming AC power is only used to charge the battery and supply the inverter. This means there's no transfer time if the main power fails. It isolates your gear from all power problems. We often use our patented technology development in these high-end systems, making them ideal for critical servers, data centers, medical equipment, and any very sensitive electronics.
| UPS Type | Power Conditioning | Transfer Time | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standby (Offline) | Basic surge/outage | 2-10ms | Low | Home PCs, non-critical devices |
| Line-Interactive | Voltage Regulation | 2-4ms | Medium | Small servers, network gear, gaming PCs |
| Online/Double-Conv | Continuous/Total | Zero | High | Critical servers, data centers, medical eq. |
Are UPS systems necessary?
You might think, "Do I really need another gadget? Power here is pretty stable." But even short flickers can cause data loss, or worse, damage your sensitive electronics over time.
Yes, UPS systems are necessary if you want to protect valuable electronics from power outages, surges, and brownouts. They prevent data loss, hardware damage, and ensure continuous operation for critical tasks.

From my experience at DAOPULSE, I can tell you that UPS systems are not just a luxury; they are often a necessity. Think about the cost of losing unsaved work. Or imagine the downtime if a server crashes. These things can be much more expensive than the UPS itself.
Power problems are more common than you might think. They include:
- Blackouts: Complete loss of power.
- Brownouts (Sags): Drops in voltage that can stress components.
- Surges (Spikes): Sudden increases in voltage that can fry circuits.
- Line Noise: Electrical interference that can corrupt data.
A UPS protects against all of these. For a home user, it might mean saving your game or finishing a document. For a business, like the hospital infrastructure company Mr. Li works for, it means keeping critical systems online. He needs suppliers with proven compliance (ISO, CE, RoHS) because the stakes are so high. Data centers, financial institutions, and construction companies all rely on UPS systems to prevent catastrophic failures. Our comprehensive testing and certification processes ensure our UPS units meet these rigorous demands. Even if your power seems stable, a single unexpected event can be disastrous. A UPS is like insurance for your electronics and your productivity.
What is an example of a UPS system?
The term "UPS system" might sound very technical and big. It's hard to picture what it actually is and what parts are involved, especially for larger setups.
A simple example is a desktop computer, monitor, and modem plugged into a line-interactive UPS unit. A more complex system includes the UPS, battery cabinets, switches, and a power distribution setup for a data center.

Let's start with a basic example. Imagine you have a desktop computer at home. A typical UPS system for this would be a small box, maybe the size of a shoebox or a bit larger. You plug the UPS into the wall outlet. Then, you plug your computer, monitor, and maybe your internet modem and router into the outlets on the UPS. This is a complete, albeit small, uninterruptible power supply system. If the power goes out, the UPS battery kicks in and keeps those devices running for a few minutes, so you can save your work and shut down safely.
Now, let's consider a much larger scale, which is where the insight about a "complete power distribution system" really comes into play. For a data center or a hospital, the "UPS system" is much more than just one box. It involves:
- The UPS Unit(s): These are much larger, often rack-mounted or even room-sized, capable of handling kilowatts or megawatts of power. Sometimes, multiple UPS units are used together for redundancy (N+1 setup).
- Batteries: These are typically housed in separate battery cabinets. There can be many strings of batteries to provide the required runtime, which could be minutes or even hours.
- Battery Switches/Breakers: These are needed to safely connect, disconnect, and isolate battery banks for maintenance or replacement.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): The output from the large UPS is fed into PDUs, which then distribute the protected power to the individual servers, network switches, and other critical loads.
- Monitoring and Management Software: This allows IT staff to see the status of the UPS, battery health, load levels, and receive alerts.
At DAOPULSE, our UPS design and customization services cover this entire range. We can design a simple lead-acid battery UPS for a small office or a complex, high-efficiency lithium battery UPS solution with extensive battery banks for a major data center, tailored to specific voltage, capacity, and application needs.
Where are UPS systems used?
Many people think UPS systems are only for big IT rooms. They might not realize how many places actually depend on this technology to keep things running smoothly.
UPS systems are used in homes, offices, data centers, hospitals, banks, industrial plants, and telecommunication sites. Essentially, anywhere reliable, continuous power is critical for operations, safety, or data integrity.

UPS systems are surprisingly common. You can find them in a huge variety of places because so many activities depend on electricity.
-
Homes and Home Offices: People use them to protect personal computers, home entertainment systems, and network equipment like modems and routers. This prevents losing files or having your internet drop during an outage.
-
Small to Medium Businesses (SMBs): Offices use them for servers, workstations, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and phone systems. Downtime here means lost business.
-
Data Centers: This is a huge area for UPS systems. They protect rows and rows of servers, storage devices, and networking gear that power websites, cloud services, and corporate networks. Our clients in this sector demand robust logistics for seamless global operations.
-
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and labs use UPS systems for critical medical equipment1 like life support machines, diagnostic tools, and patient record systems. Mr. Li, the Procurement Manager at a hospital infrastructure company, knows how vital reliable power2 is here. He needs certified and trusted suppliers like DAOPULSE.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks and trading floors rely on UPS systems for their computer systems, ATMs, and security systems to ensure transactions are processed and data is secure.
-
Industrial and Manufacturing: Factories use UPS systems for process control computers, robotics, and safety systems to prevent costly interruptions and accidents.
-
Telecommunications: Cell towers and communication hubs need UPS systems to keep phone lines and internet services running, especially during emergencies.
Our global reach at DAOPULSE means we've supplied customized UPS solutions for critical infrastructure projects in many of these areas. Our advanced facilities can adapt production to client-specific needs, from small-batch trials to full-scale manufacturing.
Conclusion
UPS systems are vital for protecting electronics and ensuring uptime. They come in different types and sizes, suitable for various needs, from home use to large-scale industrial applications.

