Data centers are complex, and "infrastructure" can sound vague. This uncertainty can make critical decisions challenging. Understanding its meaning clarifies everything for reliable operations and smart investments.
Data center infrastructure means all the physical parts that support IT operations. This includes IT hardware, power systems like UPS and generators, cooling systems, physical security, and the building itself.
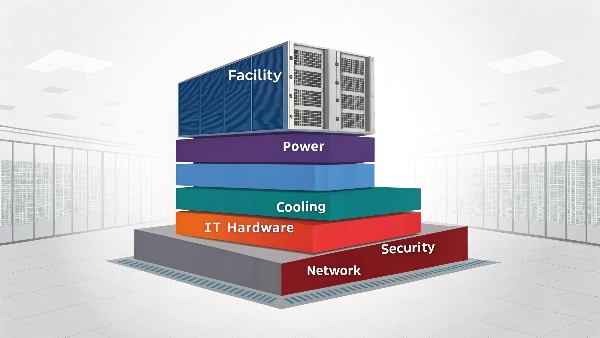
Transition Paragraph:
At Daopulse, we've spent over 10 years as an OEM/ODM manufacturer of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). During this time, I've seen how data center infrastructure has become more and more important. The demands on these facilities are huge. For Procurement Managers or System Integrators, understanding every layer of this infrastructure is key. It helps ensure that the critical systems you're responsible for, especially power systems, are robust and reliable. This article will explore these layers so you know exactly what we're talking about when we say "data center infrastructure."
Can I build a data center in my home?
Thinking of a powerful home lab? Maybe even a mini data center in your spare room? But true data center requirements are vast, complex, and often underestimated by enthusiasts. Let's explore what really separates a home setup from a genuine data center.
While you can build a powerful home server setup, it won't replicate a true data center's redundancy, security, power, and cooling infrastructure, which are essential for high availability and business operations.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
So, you're wondering if that high-powered computer setup in your basement qualifies as a data center? While it might be impressive for home use, a true data center is a different beast altogether. I've had clients at Daopulse who initially underestimated this difference. One, a small business owner, tried running critical applications from a "beefed-up" home server. A simple neighborhood power outage cost them dearly. That incident really highlighted the need for proper infrastructure, including certified UPS systems like ours.
What really defines a "real" data center? It's about achieving specific operational standards.
- Redundancy: This is key. Data centers have backups for everything – power (multiple utility feeds, redundant UPS systems, generators), cooling (multiple AC units), and network connections.
- Security: We're talking about more than a locked door. Think biometric access, surveillance, and robust cybersecurity.
- Scalability: Data centers are designed to grow and adapt to changing needs.
- Compliance: Many data centers must meet industry-specific regulations.
Let's compare a home setup to a professional data center:
| Feature | Home Setup | Data Center (Small to Large) |
|---|---|---|
| Power | Single utility line, maybe a small consumer UPS | Dual utility feeds, large commercial UPS (like our lead-acid or lithium solutions), backup generators |
| Cooling | Room air conditioning, fans | Precision CRAC/CRAH units, hot/cold aisle containment, sometimes liquid cooling |
| Security | Basic door lock, software firewall | Multi-layer physical security, advanced firewalls, intrusion detection, often 24/7 monitoring |
| Uptime/Reliability | Best effort, prone to common outages | Designed for high availability (e.g., 99.9% to 99.999% uptime), Service Level Agreements (SLAs) |
| Maintenance | DIY, as needed | Scheduled preventative maintenance by trained professionals |
So, while your home lab is great for learning and personal projects, it lacks the robust, redundant, and secure infrastructure of a true data center.
What is the data center power market size?
Data centers consume enormous amounts of electricity. This makes you think the market for their power systems must be huge. But just how big is it, and what forces are driving its continued expansion? Understanding the market size reveals its critical economic importance and future trends.
The global data center power market is valued in the tens of billions of U.S. dollars. It is projected for significant continued growth, driven mainly by cloud computing, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and the ever-increasing demand for digital services.
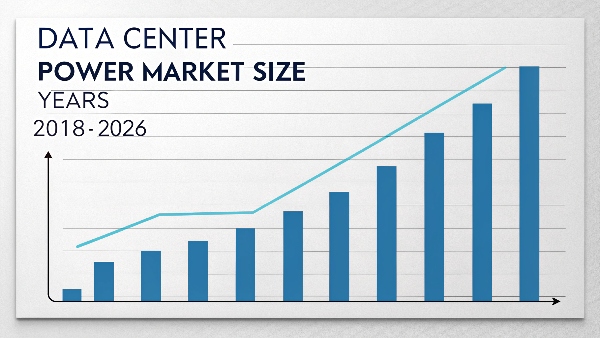
Dive deeper Paragraph:
The market for data center power systems is indeed massive and constantly growing. At Daopulse, we see this firsthand through the increasing demand for our OEM/ODM UPS solutions, both lead-acid and advanced lithium battery types. This market covers several key components:
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): This is a major segment, ensuring continuous power.
- Generators: For long-duration backup.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): For managing power at the rack level.
- Switchgear and Transformers: For managing and distributing high-voltage power.
- Monitoring Software: For overseeing power system performance.
Several powerful trends are fueling this market's expansion:
- Cloud Computing: The huge growth of cloud services from providers like AWS, Azure, and Google means they are constantly building and upgrading hyperscale data centers, all needing massive power infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These technologies require very powerful, and therefore power-hungry, servers and GPUs.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Billions of connected devices are generating vast amounts of data that needs to be processed and stored, driving demand for more data center capacity.
- Edge Computing: The need for faster processing closer to users is leading to the growth of smaller, distributed edge data centers, each requiring its own power systems.
For Procurement Managers and System Integrators, this dynamic market means new technologies and solutions are always emerging. Staying informed about advancements, for example, the benefits of lithium-ion UPS systems for total cost of ownership and efficiency, is vital.
| Power Market Component | Key Growth Driver(s) | Our Contribution at Daopulse |
|---|---|---|
| UPS Systems | Need for uptime, power quality, energy efficiency | Core offering: design & manufacture of reliable, certified UPS |
| Backup Generators | Protection against extended utility outages | Our UPS systems integrate seamlessly with generators |
| PDUs | Efficient power distribution within racks | Complements our UPS solutions for full power path |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Grid stability, renewables integration, peak shaving | Our lithium battery UPS tech contributes to this |
The global nature of this market also means suppliers need to meet international standards, like the CE, RoHS, and ISO certifications that Daopulse holds.
How to fully document a data center?
Managing a data center without clear, comprehensive documents is like navigating a city without a map – it's chaotic. This lack of clarity leads to errors, slow troubleshooting, and inefficient operations. Proper documentation is your essential roadmap to efficiency, control, and reliability.
Fully documenting a data center involves detailing all IT assets, network topology, power paths (including UPS and PDU layouts), cooling systems, physical layouts, security procedures, and maintenance logs. This is often managed using DCIM software.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Comprehensive documentation is not just a 'nice-to-have'; it's a fundamental requirement for any well-run data center. I always stress this to clients who purchase our UPS systems from [Your Company Name]. Knowing exactly how our UPS units fit into their overall power scheme is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Why is documentation so important?
- Troubleshooting: When something goes wrong, good documentation helps pinpoint the problem quickly.
- Change Management: Planning upgrades, adding new equipment, or moving services becomes much easier and less risky.
- Capacity Planning: Understand current utilization of power, space, and cooling to plan for future needs.
- Compliance and Audits: Many industries require detailed records for regulatory compliance.
- Onboarding: Helps new team members get up to speed quickly.
So, what exactly should be documented? Here are some key areas:
| Documentation Area | What to Include | Why It's Critical for Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Layout | Rack elevations, floor plans showing equipment locations, aisle designations. | Efficient space utilization, locating equipment. |
| IT Asset Inventory | Details for servers, storage, network gear (make, model, serial no., OS, IP, applications hosted, owner). | Lifecycle management, impact assessment. |
| Network Topology | Logical and physical network diagrams, IP address schemas, VLAN configurations, port mappings. | Troubleshooting connectivity, security planning. |
| Power Infrastructure | Utility feeds, UPS systems (model, capacity, battery type & age, maintenance logs – vital for our UPS users!), PDUs, generator details, circuit breaker panels. | Tracing faults, planning maintenance, ensuring uptime. |
| Cooling Systems | Locations of CRAC/CRAH units, AHUs, chillers; airflow diagrams, temperature/humidity sensor locations & setpoints. | Maintaining optimal environment, energy efficiency. |
| Cabling Infrastructure | Cable types, paths, labeling conventions, patch panel connections. | Simplifying moves, adds, and changes. |
| Procedures & Policies | Maintenance schedules, disaster recovery plans, security protocols, escalation procedures. | Standardized operations, risk mitigation. |
Tools like Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) software are invaluable for larger facilities, but even well-organized spreadsheets and diagramming tools can work for smaller setups. The key is consistency and keeping it up-to-date.
How are AHUs used in data centers?
Data centers generate an incredible amount of heat. Effective cooling is absolutely non-negotiable to prevent equipment damage. If this heat isn't managed properly, it quickly leads to overheating and system failures. Air Handling Units (AHUs) are key players in maintaining the ideal environment.
Air Handling Units (AHUs) in data centers circulate, filter, and condition air. They typically work with chillers or direct expansion (DX) systems to precisely control temperature and humidity, ensuring optimal operating conditions for sensitive IT equipment.
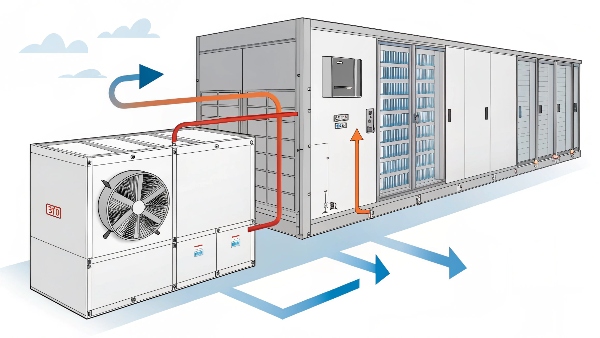
Dive deeper Paragraph:
Air Handling Units1, or AHUs, are a critical part of the cooling puzzle in many data centers. While Computer Room Air Conditioners (CRACs) or Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAHs) are often seen on the data center floor directly managing the air for the IT equipment, AHUs play a broader role, especially in larger facilities. They are essentially large metal boxes containing:
- Blowers/Fans: To move large volumes of air.
- Heating/Cooling Coils: To change the air temperature. In data centers, it's primarily cooling coils2, fed by chilled water or refrigerant.
- Filters: To remove dust and particulate matter.
- Humidifiers/Dehumidifiers: To control moisture levels.
- Dampers: To control airflow paths and mix fresh air with recirculated air.
Their main functions in a data center environment are:
- Temperature Control: They distribute cooled air, helping to maintain the precise temperatures required by sensitive IT gear.
- Humidity Control: Keeping relative humidity within the ideal range (often 40-60%) is vital. Too low can cause static electricity; too high can lead to corrosion.
- Air Filtration: Clean air is essential to prevent dust buildup on electronics, which can cause overheating or shorts.
- Ventilation & Air Circulation: Ensuring a consistent supply of fresh, conditioned air and preventing hot spots.
It's important to note that cooling systems themselves need reliable power. At Daopulse, we often find our UPS systems are specified not just for the IT load but also to support critical cooling components. A System Integrator knows that if the cooling goes down because of a power blip, the IT equipment will quickly follow. This integrated approach to power and cooling is essential for overall data center resilience.
| AHU Function | Data Center Benefit | Consequence of Malfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintains optimal IT operating conditions | Equipment overheating, reduced lifespan, failure |
| Humidity Control | Prevents electrostatic discharge (ESD) & corrosion | Component damage, data errors |
| Air Filtration | Protects electronics from harmful contaminants | Overheating, short circuits, reduced reliability |
| Air Circulation | Ensures even cooling, prevents hot spots | Localized overheating, inefficient cooling |
AHUs are often part of a larger, sophisticated HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) strategy, working in concert with other cooling technologies to keep the data center running smoothly.
Conclusion
Data center infrastructure is complex, covering everything from the building to power, cooling, and IT gear. Each part is vital, working together to support our digital world's demands.

