Power outages or disturbances can wreak havoc on critical electrical systems. This disruption often leads to significant financial losses and operational chaos. A UPS system provides the essential shield, ensuring your electrical equipment stays powered and protected.
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system for electrical applications is a device that provides emergency power and power conditioning to connected equipment. It ensures a continuous, clean supply of electricity, safeguarding against outages and quality issues.

At DAOPULSE, we've dedicated a decade to mastering the art and science of uninterruptible power supplies. We see them as more than just backup; they are crucial for the seamless operation of any modern electrical infrastructure. Large industrial setups and critical medical equipment, for instance, often rely on robust three-phase UPS systems. When clients like Mr. Li, a Procurement Manager at a hospital infrastructure company, approach us, they are looking for reliability and tailored solutions. We understand that each electrical environment has unique demands, and our role as an OEM/ODM manufacturer is to provide specific power solutions, whether it's designing a custom UPS or ensuring our lead-acid or lithium battery options perfectly fit the application.
What does UPS mean electricity?
The acronym "UPS" gets thrown around a lot in electrical discussions. If its meaning isn't clear, you might misunderstand its vital role in protecting your valuable electrical assets and operations.
In electricity, UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply. It signifies a system designed to maintain a continuous supply of electrical power to connected equipment, even if the primary power source fails or fluctuates.

So, UPS literally means the power won't be interrupted. But it's about more than just keeping the lights on during a total blackout. A true UPS, especially the Online Double-Conversion1 types we specialize in at DAOPULSE, acts as a constant buffer between the often unpredictable utility power and your sensitive electrical loads. It takes the incoming AC power, converts it to DC to charge its batteries and power its inverter, and then the inverter reconverts clean, stable AC power to your equipment. This process inherently provides excellent power conditioning2. This means it smooths out sags (low voltage), swells (high voltage), filters out electrical noise, and can even correct frequency variations. For delicate electronics, PLCs in a factory, or life-saving medical devices, this high-quality, stable power is just as important as the backup function. Procurement managers value this because it minimizes risks associated with poor power quality, and our CE, RoHS, and ISO certifications provide them with the assurance that our systems deliver on this promise consistently. Our 10 years of experience have taught us that "uninterruptible" also means "undisturbed" and "uncompromised" power.
What is a 3-phase UPS system?
For small offices, a single-phase UPS is fine. But for larger electrical loads in industry or big facilities, using a single-phase UPS can lead to overload, inefficiency, or an inability to power the equipment at all.
A 3-phase UPS system is an uninterruptible power supply designed to support equipment that requires three-phase electrical power. This is common for high-capacity loads found in industrial settings, data centers, and large commercial buildings.

Three-phase power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It provides more power, more consistently, than single-phase power. Think of single-phase as one person pedaling a bike, and three-phase as three people pedaling in a coordinated rhythm – it's smoother and can deliver much more power. Many large electrical motors, HVAC systems, medical imaging machines (like MRIs and CT scanners), and entire data center server racks are designed to run on three-phase power. Attempting to power these with a single-phase UPS simply won't work or will be highly inefficient. As mentioned in my insight, large industrial and medical equipment almost always needs three-phase UPS. At DAOPULSE, we have extensive experience designing and manufacturing robust three-phase UPS systems. Our advanced facilities can produce a wide range of these units, tailored to specific client requirements, including voltage, capacity, and whether lead-acid or advanced lithium battery UPS solutions are more appropriate. System integrators working on critical infrastructure projects for data centers, hospitals, banks, or commercial buildings rely on us for these high-capacity, reliable power solutions. We ensure our patented technology development contributes to the efficiency and reliability of these larger systems.
Which type of UPS is better?
With so many UPS types available – standby, line-interactive, online – it's easy to get lost. Choosing the wrong one means you might overspend for features you don't need, or worse, under-protect your critical electrical systems.
There isn't one single "better" type of UPS; the best choice depends entirely on the sensitivity of the electrical load, the level of protection required, budget, and the specific application's environment.
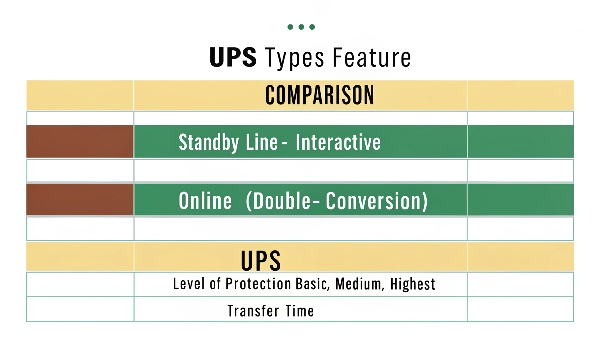
The question "Which type of UPS is better?" is one I hear often. The answer always starts with, "It depends on what you're trying to protect." Let's break down the main types:
-
Standby (or Offline) UPS: This is the most basic type. It passes utility power directly to the load under normal conditions, with some surge protection. If a power failure occurs, it quickly switches to battery power.
- Pros: Least expensive, good for non-critical loads like a basic home office PC.
- Cons: Has a brief transfer time (a few milliseconds) which some sensitive equipment might not tolerate. Offers minimal power conditioning beyond surge suppression.
-
Line-Interactive UPS: This type includes an Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR). It can correct minor power fluctuations (sags and swells) without switching to battery, preserving battery life. It still has a transfer time when switching to full battery backup.
- Pros: Better voltage regulation than standby, moderately priced. Good for small business servers, network equipment, and point-of-sale systems.
- Pros: Still has a transfer time to battery. Waveform on battery might not be pure sine wave on all models.
-
Online (or Double-Conversion) UPS: This type provides the highest level of protection. The inverter is always on, constantly regenerating a clean, stable sine wave output from the incoming AC (which is first converted to DC). There is zero transfer time to battery because the load is always running off the inverter.
- Pros: Highest level of power protection and conditioning, no transfer time, pure sine wave output. Ideal for critical loads, sensitive electronics, medical equipment, data centers, and industrial controls.
- Cons: Generally more expensive and can be slightly less efficient (though modern designs, like those incorporating our patented technology at DAOPULSE, are highly efficient).
For most industrial and critical electrical applications that our clients like Mr. Li (Procurement Manager) deal with, an Online Double-Conversion UPS is typically the "better" and often necessary choice. We specialize in these, offering both lead-acid and lithium battery UPS solutions. Our team provides reliable technical support to help clients assess their needs and select the most cost-effective and technically appropriate UPS type.
What is the primary use of UPS?
Many think a UPS is only for blackouts. This narrow view means they might miss out on protecting their electrical systems from a whole range of other, more common, power problems that can cause damage.
The primary use of a UPS is to ensure a continuous and high-quality supply of electrical power to critical equipment, protecting it not only from complete outages but also from various power disturbances.
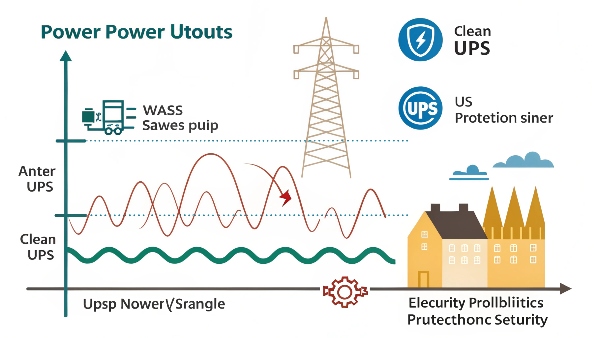
While providing backup power during a complete outage (a blackout) is a very visible function, the primary use of a UPS, especially an Online Double-Conversion model, extends far beyond that. It's about comprehensive power quality and continuity. Here's what a good UPS system, like those we design and manufacture at DAOPULSE, protects your electrical equipment from:
- Power Failure (Blackout): Total loss of utility power.
- Power Sag (Brownout): Short-term low voltage.
- Power Surge (Swell): Short-term high voltage.
- Under-voltage: Sustained low voltage.
- Over-voltage: Sustained high voltage.
- Electrical Line Noise: Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI).
- Frequency Variation: Deviations from the nominal power frequency (e.g., 50Hz or 60Hz).
- Switching Transients: Instantaneous under or over-voltages.
- Harmonic Distortion: Distortion of the normal power waveform by non-linear loads.
These power problems are far more common than complete blackouts and can degrade, damage, or disrupt the operation of sensitive electrical and electronic equipment over time. For a System Integrator working on a data center or a Procurement Manager sourcing equipment for a hospital, ensuring protection against this full spectrum of issues is paramount. Our UPS systems, backed by CE, RoHS, and ISO certifications, are engineered to provide this comprehensive protection. This is part of establishing stable long-term partnerships, supporting continuous growth and innovation for our clients.
Conclusion
A UPS system is crucial for electrical setups, offering vital backup and power conditioning. Understanding its meaning, types like 3-phase, and its primary uses ensures reliable, clean power for all critical applications.

