Building a PC with a 600W power supply? Choosing the right UPS is crucial to protect your investment, but navigating VA ratings and power factors can be confusing, risking underpowering or overspending.
For a PC with a 600W PSU, aim for a UPS with at least 900VA to 1000VA and a true wattage rating comfortably above 600W. This ensures sufficient power and a buffer for peripherals and efficiency.

From my experience as an OEM/ODM manufacturer at DDAOPULSE for the past decade, I've seen that for a general office computer or a mid-range build, a 1000VA (1kVA) UPS often hits the sweet spot—it's economical and provides adequate protection and runtime for a safe shutdown. Of course, opting for a larger UPS is always possible and offers more runtime or capacity for additional peripherals. The key is understanding that the wattage of your PC's power supply unit (PSU) isn't the only number to consider; you need to look at the UPS's actual watt output capability and its VA rating. For a 600W build, simply getting a 600VA UPS would be a mistake.
What UPS do I need for a 600W PC?
Got a 600W PSU in your PC? Selecting the wrong UPS could mean your PC shuts down unexpectedly during an outage, or you might overpay for capacity you don't need.
For a 600W PC, you need a UPS with a true output wattage comfortably above 600W. This often translates to a UPS rated around 900VA to 1200VA, depending on its power factor.

When you have a PC with a 600-watt power supply unit (PSU), it's important not to pick a UPS that is also just rated at 600 Watts or, even worse, 600 VA. Here's the breakdown:
- PSU Wattage vs. Actual Draw: Your 600W PSU rating is its maximum output capacity. Your PC won't constantly draw 600W. Under normal load, it might draw 200-400W, and only approach 600W (or slightly more for very brief peaks if the PSU is high quality) under extreme load like intense gaming or heavy processing.
- UPS Wattage Rating1: This is the crucial number. The UPS must be able to supply at least the maximum power your PC will actually draw, plus a little headroom.
- UPS VA (Volt-Amps) Rating: UPS systems are also rated in VA. The relationship between VA and Watts is determined by the UPS's power factor (PF)2. Watts = VA * PF. Common power factors for consumer UPS units range from 0.6 to 0.9 (or even 1.0 for some premium online UPS models).
So, if a UPS has a power factor of 0.7 and is rated at 1000VA, its wattage output is 1000 * 0.7 = 700 Watts. This would be a good starting point for a 600W PC system.
At DAOPULSE, we often guide our clients, like system integrators building custom rigs or procurement managers outfitting offices, to select a UPS with a wattage rating about 20-25% higher than the PC's PSU rating to account for peripherals (monitor, modem), PSU efficiency, and to ensure the UPS isn't running at its absolute maximum capacity, which can shorten its life. For a 600W PC, a UPS that can deliver around 650-750W (which might be a 1000VA to 1200VA unit, or even a 1500VA unit if you want longer runtime) is a safe bet. Our UPS design and customization capabilities allow us to tailor solutions, including lead-acid or lithium battery UPS options, to perfectly match these needs.
| PC PSU Rating | Typical UPS VA Range (assuming PF 0.6-0.7) | Typical UPS Wattage Range | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 600W | 900VA - 1500VA | 540W - 1050W | Aim for actual UPS wattage > 600W, ideally 650W-750W+ |
| Example | 1000VA (PF 0.7) | 700W | Good match for a 600W PC, allows for monitor |
| Example | 1200VA (PF 0.6) | 720W | Good match |
| Example | 1500VA (PF 0.65) | 975W | Excellent, offers more headroom/runtime |
How big of an UPS do I need for my PC?
Choosing a UPS size feels like a guessing game? Get one too small, and it's useless. Too big, and you've wasted money. Finding that "just right" size is key for effective protection.
To size a UPS for your PC, calculate the total wattage of your PC and essential peripherals (like monitors). Then, choose a UPS with a wattage rating at least 20-25% higher than this total.
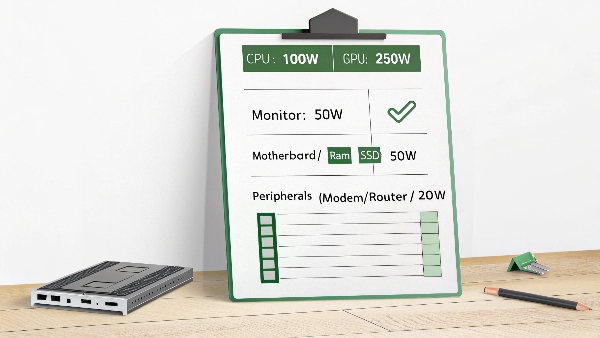
Determining the right "size" for your UPS involves a few steps beyond just looking at your PC's PSU wattage:
-
Calculate Your Total Load in Watts:
- PC: While your PSU might be 600W, your PC's actual average and peak draw are usually less. However, for sizing, it's safer to use a figure closer to the PSU's rating, or use an online power supply calculator to get a more accurate estimate based on your specific components (CPU, GPU, etc.).
- Monitor(s): An LCD/LED monitor can draw anywhere from 20W to 100W+ depending on size and brightness. Check its specifications.
- Other Essential Peripherals: Include your modem, router, and perhaps external hard drives if you want them to stay powered. Do not include laser printers on the battery backup outlets.
- Sum these wattages. For example, a 600W PSU PC (let's assume peak draw is around 500-550W for safety), a 50W monitor, and 20W for modem/router = 570-620W.
-
Apply a Buffer: Choose a UPS with a wattage output that is at least 20-25% higher than your calculated total load. For 620W, a 25% buffer would mean looking for a UPS that can output around 775W (620 * 1.25).
-
Check VA Rating and Power Factor: UPS units are often advertised by their VA rating. Ensure the wattage rating (VA * Power Factor) meets your calculated need with the buffer. A 1200VA UPS with a 0.7 power factor provides 840 Watts, which would be suitable. A 1000VA UPS with a 0.8 PF provides 800W, also good.
-
Consider Runtime: If you need more than 5-10 minutes of runtime, you'll need a UPS with larger internal batteries or the option to add external battery modules (EBMs). This often means a higher VA/Wattage model. At DAOPULSE, we offer both lead-acid battery UPS and lithium battery UPS solutions, where lithium can offer longer runtimes in a smaller footprint. Our patented technology development often focuses on improving efficiency, which can also contribute to better runtime.
Is 600 watts a lot for a PC?
Looking at a 600W power supply for your PC build? You might wonder if this is overkill, just right, or not enough, especially considering energy costs and component needs.
600 watts is a moderate and common PSU size for many mid-range to upper-mid-range PCs, especially those with a decent dedicated graphics card. It's not excessively high but provides good headroom for many builds.

Whether 600 watts is "a lot" for a PC is relative to the components inside it. Here's a general perspective:
- Basic Office/Web Browsing PC: For a computer with integrated graphics, a modest CPU, one SSD, and minimal peripherals, 600W is definitely overkill. These systems often run efficiently on 300W-400W PSUs.
- Mid-Range Gaming PC / Content Creation PC: This is where a 600W PSU often fits well. If you have a mid-tier CPU (like an Intel Core i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen 5/7) and a dedicated graphics card (e.g., NVIDIA GeForce RTX xx60/xx70 series or AMD Radeon RX 6x00 series), a 600W PSU provides adequate power with some headroom for future upgrades or peak loads.
- High-End Gaming PC / Workstation: For top-tier CPUs, very powerful graphics cards (e.g., RTX xx80/xx90 series or high-end Radeon cards), multiple drives, and overclocking, 600W might be cutting it close or could be insufficient. These systems often benefit from 750W, 850W, or even 1000W+ PSUs.
So, 600W is not considered "a lot" in an absolute sense for modern PCs that include a dedicated graphics card for gaming or professional work. It's a very common and sensible choice for a wide range of capable machines. At DAOPULSE, when we design customized UPS solutions for clients procuring systems for entire offices or specific departments, we often see PCs in this power range. Ensuring they have reliable power from our CE, RoHS, and ISO certified UPS units is crucial for their productivity. The key is that the PSU should always be rated higher than the system's expected peak draw to ensure stability and efficiency. A 600W PSU gives a good buffer for a system that might typically peak around 400-500W.
Can 600VA UPS enough for a gaming PC?
Eyeing a 600VA UPS for your gaming rig? The attractive price might be tempting, but this could be a critical misstep, leaving your expensive components vulnerable when you need protection most.
No, a 600VA UPS is almost certainly not enough for a modern gaming PC, especially one that might have a 600W PSU. The actual wattage output of a 600VA UPS is typically much lower (e.g., 300-360W).

This is a very important distinction: VA (Volt-Amps) is not the same as Watts. A 600VA UPS will not safely power a gaming PC that has, for instance, a 600W power supply unit (PSU) or even a system that consistently draws 400-500W during gameplay.
Here's why:
-
Power Factor: As mentioned before, UPS systems have a power factor (PF) which is less than 1.0 (often 0.6 to 0.7 for consumer-grade VA-rated units). The actual power a UPS can deliver in Watts is VA multiplied by PF.
- So, a 600VA UPS with a typical power factor of 0.6 only delivers 600 * 0.6 = 360 Watts.
- Even with a slightly better PF of 0.7, it's only 600 * 0.7 = 420 Watts.
-
Gaming PC Power Draw: Modern gaming PCs, especially those with dedicated graphics cards, can draw significant power, easily exceeding 360W or 420W under load. A PC with a 600W PSU might peak close to that or consistently run at 300-500W while gaming.
-
Overload Risk: If you connect a gaming PC that draws more watts than the UPS can provide, the UPS will likely go into an overload state and shut down, offering no protection when you need it most (like during a power flicker while gaming). It might beep complainingly or just cut power.
For a gaming PC, particularly if it has a 600W PSU, you should be looking at a UPS rated significantly higher in VA to ensure its wattage output is sufficient. As per my insight, a 1kVA (1000VA) UPS, which might provide around 600-700W, is a much better starting point. For more powerful gaming rigs, a 1500VA UPS (providing perhaps 900-1000W) would be even safer and offer more runtime. At DAOPULSE, our team of professionals always emphasizes matching the UPS's true wattage output to the client's load, ensuring seamless project management and reliable solutions, whether they're using our cost-effective lead-acid battery UPS solutions or our high-efficiency lithium battery UPS units.
Conclusion
For a 600W PC build, a 1000VA (1kVA) UPS is often a good, economical choice, providing around 600-700W. Always prioritize the UPS's actual wattage output over its VA rating to ensure sufficient power.

